Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) progresses slowly, is often asymptomatic in early stages, but can have significant impact on quality of life (QOL) at later stages when nerve damage occurs'
Causes of PN are several

Immune-mediated conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis

Toxic substances such as alcohol.

Chemotherapy

Vitamin B deficiencies.
Viral infections
HIV
Tuberculosis

Diabetes
... Early treatment of PN is essential
International guidelines focus primarily on management of neuropathic pain, with lesser focus on treating the underlying causes which does not help restore nerve function and health
* Neurotropic B vitamins (B1, B6, and B12) are w established & used commonly for PN management.
* The prophylactic use of neurotropic B vitamins (B1 B6 and B12) is recommended
* B1, B6, and B12 may be initiated for patients w PN due to metabolic diseases, medication, nutri deficiency and other causes
* Considered safe, even at high doses and in the long term.
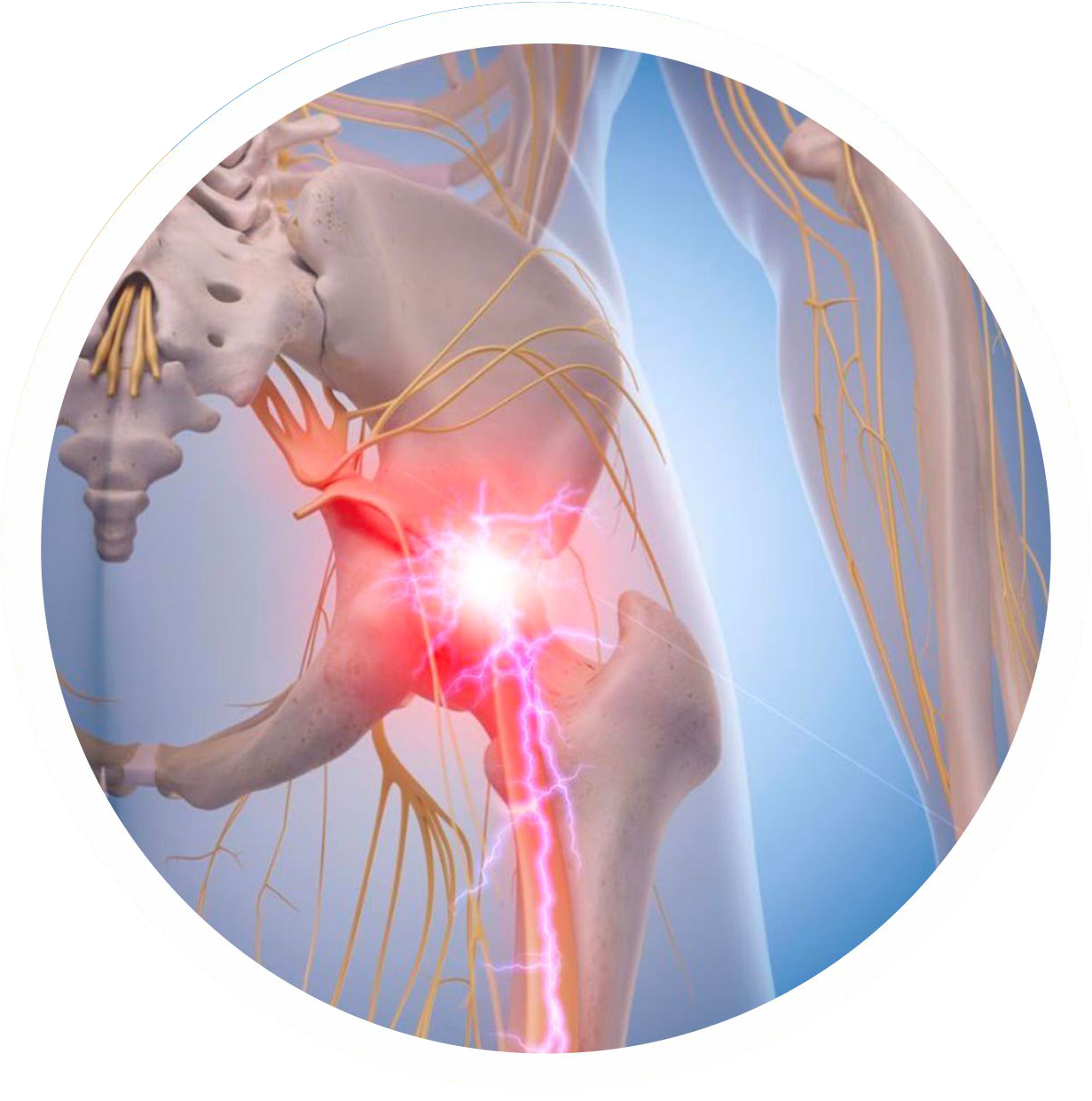
To avoid long-term consequences & impaired QOL due to chronic pain, loss of sensation & irreversible nerve damage introducing

Vitamins B1 + B6 + B12
offer synergistic effect & provide symptomatic relief effectively in PN, improve nerve function & help in nerve regeneration more effectively than individual vitamins used alone.
Indication
* Helps relieve common symptoms of B vitamin deficiency such as Tingling, Numbness and Burning sensation.
* Supportive treatment of neuritis and neuralgia (neuropathies)
* In dietary deficiencies of Vitamin B1,B6 and B12
* Anemia & Hepatitis

recommended Dose: Adults can take one tablet per day or as directed by healthcare practitioner.It is best taken with or after a meal.Swallow the tablet (without chewing) with a little water to wash it down.
To improve nerve health
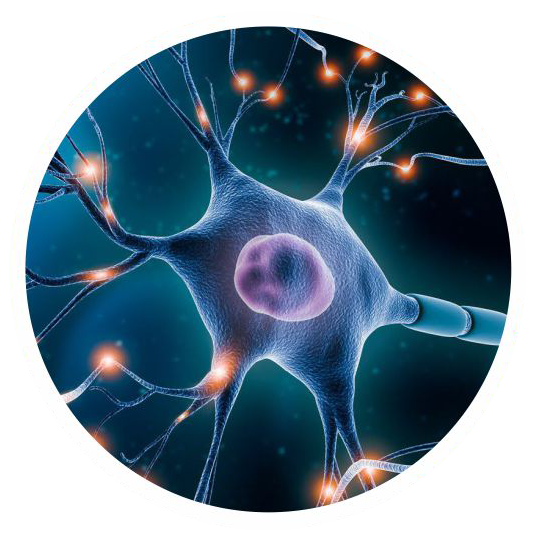

Protects and nourishes the nerves along with proper diet and exercise.
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
🔸 Plays a key role as a coenzyme in carbohydrate metabolism, which is the main energy supply for nerve fibers.
🔸 Initiates nerve impulses from coenzymes
🔸 Acts as a site-directed antioxidant, prevents nerve damage from oxidative stress
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin)
🔸 Helps regenerate and repair nerves
🔸 Plays a role in the metabolism of fatty acids which are useful in repairing & maintaining the nerve myelin fibers.
🔸 Vitamin B12 defeciency causes demyelination of nerves in the central and peripheral nervous system,loss of sensation in peripheral nerves, and weakness in the lower extremities.
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
🔸 Involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters
🔸 Helps enable the transmission of nerve signals
🔸 Balances nerve metabolism
In Peripheral Neuropathy
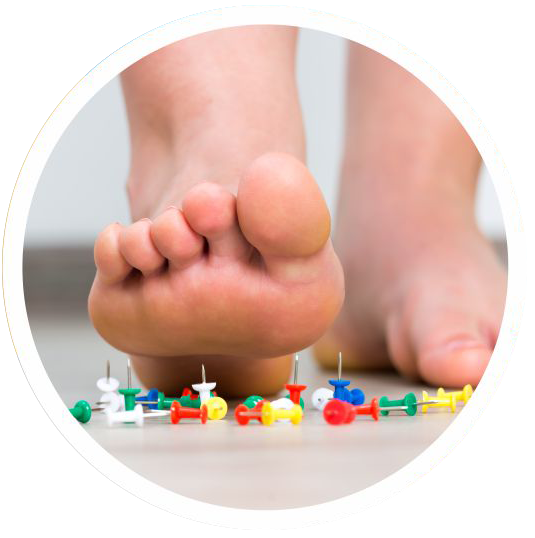

Protects and nourishes the nerves along with proper diet and exercise.
The NENOIN study
In patients with mild-to moderate PN of different etiologies,including diabetes mellitus, nutritional deficiency, alcoholism, carpal tunnel syndrome, idiopathic PN, and others.
🔸 A fixed dose combination of neurotropic B vitamins significantly reduced overall score for stabbing pain,burning pain, paresthesia, and numbness within 14 days of treatment.
Subjects diagnosed with moderate PN given vitamins B1,B6,B12 for 2 months, were evaluated on days 0,30 and 60.
🔸 Reduced symptom score of VAS in patients with peripheral neuropathy
🔸 There was an important in the TSS score (pain intensity, burning, tingling and numbness)
Diabetes is the most common cause of peripheral neuropathy, with 50% of diabetic adults affected during their lifetime.


B1,B6,B12 have a positive effect on neurophysiological symptoms and functions in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.
In a study, a combination of vitamins B1 (100mg), B6 (100mg), and B12(200mcg) was found to be effective in 57% of patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
🔸 Several studies have confirmed the benefit of continuous administration of vitamins B1,B6 abd B12 in diabetic neuropathy.
Metformin use is a risk factor for the development of diabetic Pn.
🔸 In a study, patients aged 50 years and above treated with metformin for at least 18 months were reported to be 2-3 times more likely to develop PN
🔸 Prolonged use and higher doses of metformin was associated with vitamin B12 deficiency.
Patients with TB and HIV infection may also be predisposed to developing Pn.


🔸 In patients with TB, the development of PN can be caused by the disease itself, comorbid conditions associated with TB, or the front-line anti-TB drug isoniazid.
🔸 Isoniazid depletes vitamin B6 by interference with the metabolism of vitamin B6, which may result in the development of PN.'
🔸 B-vitamin deficiencies are common in HIV- infected individuals and have been associated with increased risk of HIV disease progression
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is associated with PN

🔸 Chronic kidney disease (CKD) with a glomerular filtration rate of < 12 mL/minute is associated with clinically significant PN.
🔸 70-100% of patients with end-stage renal disease experience neuropathic symptoms.
🔸 Patients on a restricted diet, including vegetarians, have been shown to be at high risk of vitamin B12 deficiency.
🔸 Vitamin B12 helps prevent anemia is CKD patients.
Role of Neurotropic B vitamins in Bariatric surgery & Hepatic disorders


🔸 The initiation of neurotropic B vitamins (B1, B6, and B12) in patients after bariatric surgery is beneficial.
🔸 PN has been reported in 10-33% of patients who have undergone bariatric surgery, with an average time to onset of 3.7 years post surgery.
🔸 Vitamin deficiency is common in chronic liver diseases, such as alcoholic liver disease (ALD), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
🔸 B1 deficiency is common in chronic alcoholics2 * Lower serum levels of vitamin B6 and glutathione have been observed in cirrhosis.